This week on Adventures on the Bookshelf we’re continuing our exploration of the exhibition ‘Babel: Adventures in Translation‘. A couple of weeks ago, we looked at the Cinderella story and how it has been transferred and adapted across cultures. This week, we’re thinking about how to translate fables.
You probably know that a fable is a short story that aims to convey a moral, usually involving animals. Famous examples include ‘The Boy who Cried Wolf’, ‘The Town Mouse and the Country Mouse’, and ‘The Hare and the Tortoise’, to name but a few. Such stories have been popular since ancient times, and can be identified in many different traditions, including Aesop’s ancient Greek fables, and the Sanskrit Panchatantra, which are among the world’s most translated texts. These stories have enjoyed an enduring popularity and are still widely told today.
Although we might think of these stories as being primarily for children, they were originally written for adults in order to promote a moral message. But, of course, when it comes to translation, that raises all sorts of questions: how far is it possible to transfer a moral framework between different cultures and communities?; why are animals afforded such a key role in fables, and do animals have the same associations across the world?
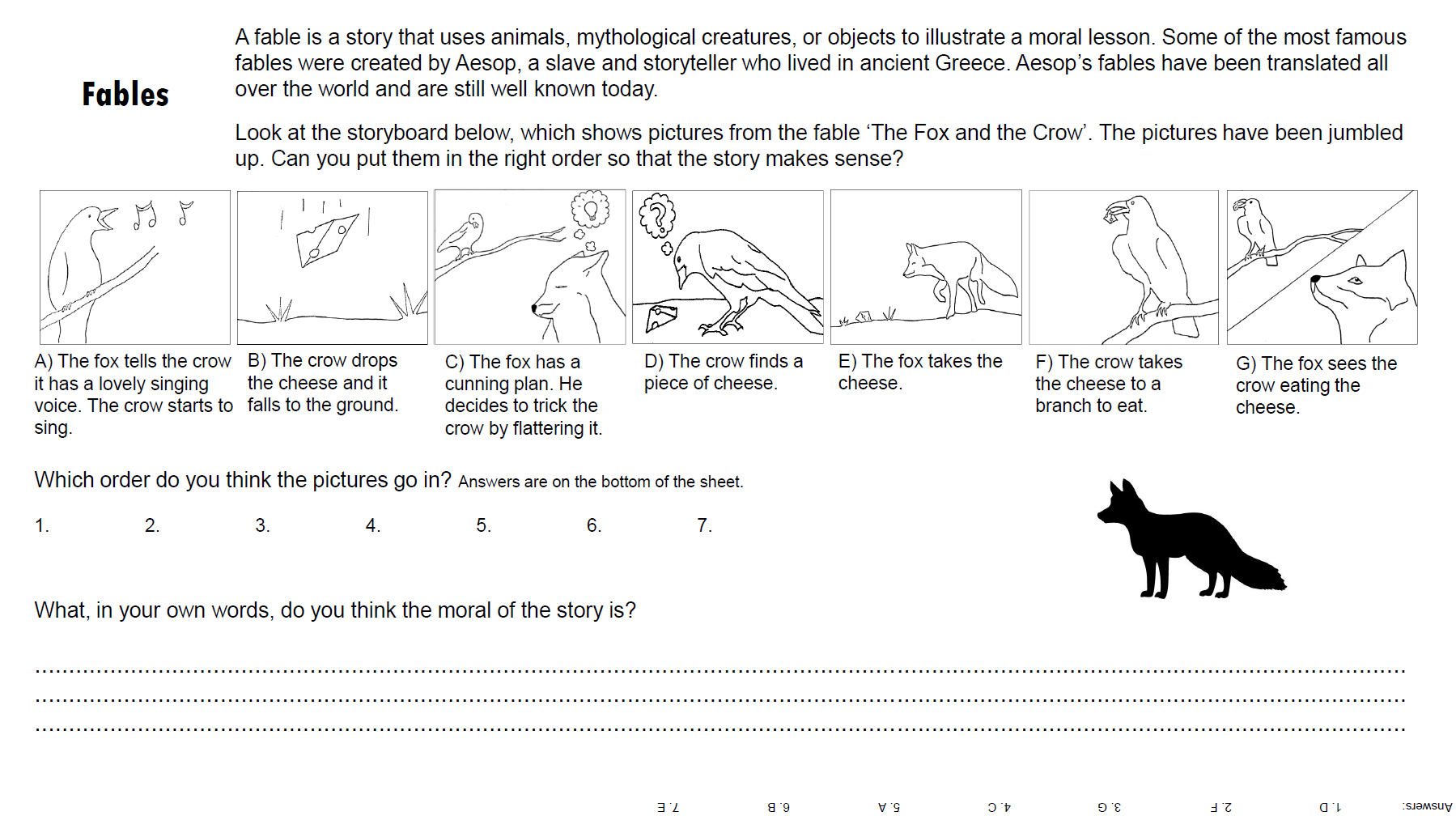
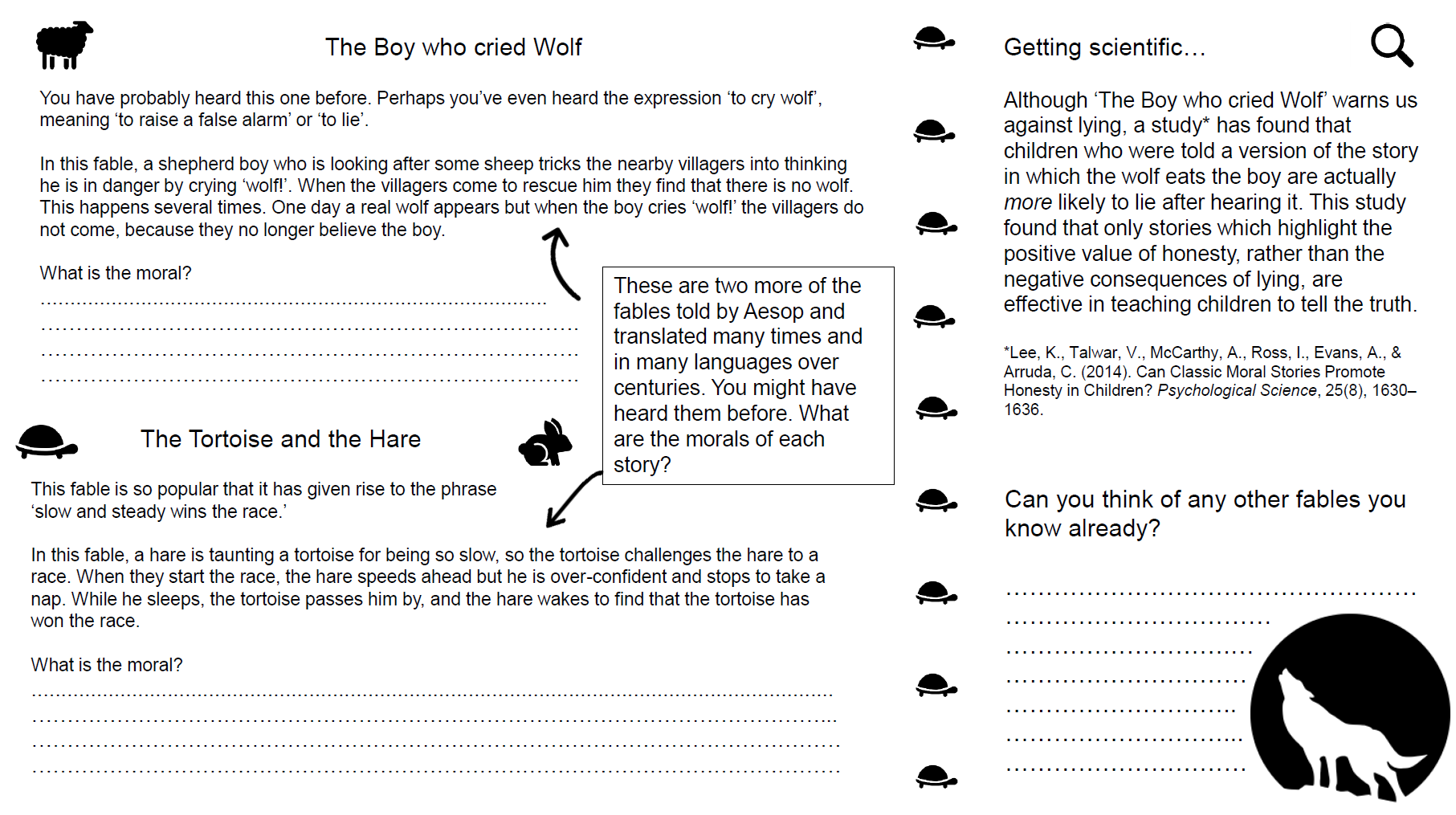
Below, we’ve included a worksheet that was designed for visitors to the exhibition. However, you do not need to have seen the exhibition to undertand it. Take a look at some of the discussion points raised, including, intriguingly, the surprising study that found that children who were told the story of ‘The Boy who Cried Wolf’ were actually more likely to lie after hearing it! You can right click and open the images separately to see a bigger version, or access a pdf here.
Remember, the exhibition runs until 2nd June – do pay a visit if you can!