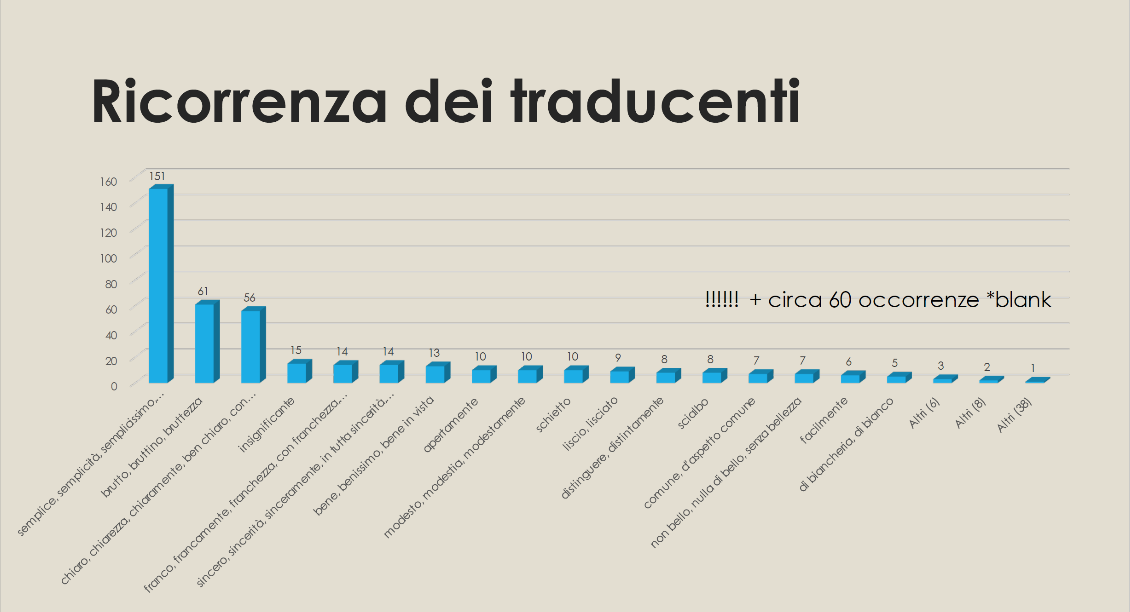
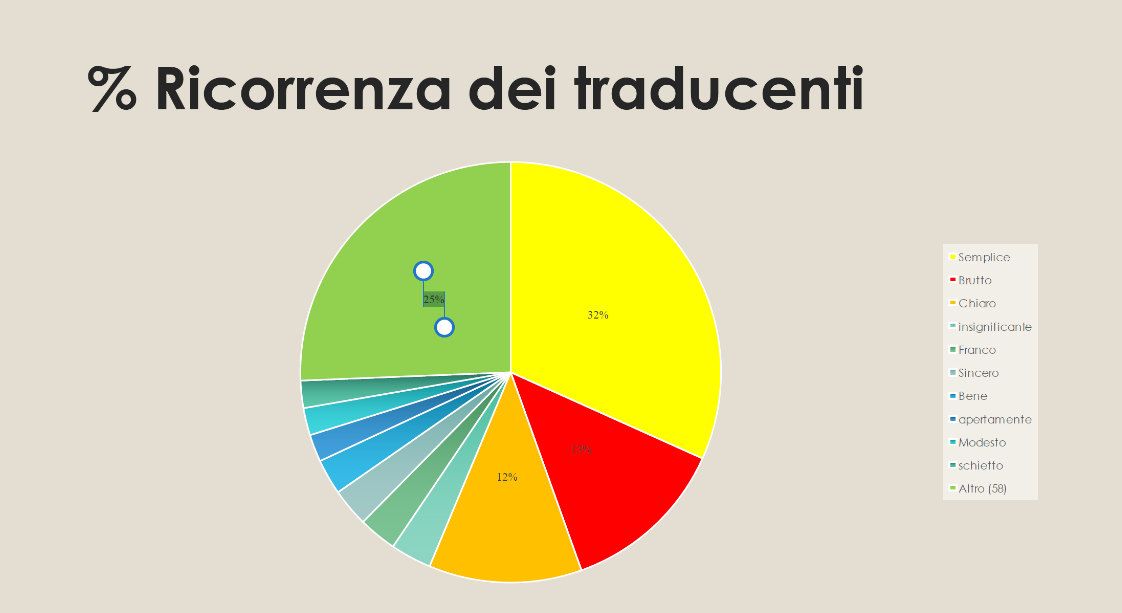
Here at the Faculty of Medieval and Modern Languages, we organise and run a range of open days for prospective students and their parents and guardians. Open days are one of the best ways to get a real feel for a University, helping students to make informed decisions about their futures.
Over the course of February and March, we will be holding our language-specific open days, designed to provide greater insight into our undergraduate degree programmes. In comparison to our wider open day in May, language-specific open days are smaller and more focused in their scope, allowing more time to explore a subject in depth.
For example, the German open day offers an introduction to German film, linguistics, and different types of literature. On the Spanish and Portuguese open day, you can explore medieval Iberian literature and learn Portuguese in 15 minutes. The Italian open day will introduce you to Italian literature’s biggest names from the Middle Ages and Renaissance periods.
So, if you’re thinking about applying to study languages at Oxford, or want to find out more about a particular course, these open days offer a wonderful opportunity to meet some of our tutors and current students, come along to academic taster sessions which will give you a flavour of what it’s like to study languages, and ask lots of questions.
Below are the details of our 2022 language specific open days. You will need to book a place at these events, which you can do via our open day website, where you will also find the event programmes.
- German: Saturday 19th February, 11am – 3pm, Microsoft Teams
- Spanish & Portuguese: Friday 25th February, 10am-3pm, St Anne’s College
- Italian: Saturday 5th March, 11am-1.30pm, Microsoft Teams
- Russian and Slavonic Languages: Saturday 5th March, further details to be published soon.
You may have noticed that there is no specific open day for French: students interested in French should attend the Faculty’s main open day in May or one of the University open days in July or September. Keep your eyes peeled for more information about those events in future blog posts.
We look forward to having you along to our language-specific open days – don’t forget to book your place!
While you’re here: a reminder that applications to our 2022 UNIQ programme are still open! You can read more about this fantastic opportunity for UK state school students in last week’s blog post, or head to the website for further information.