This post was originally published on the Creative Multilingualism blog. Creative Multilingualism is a four-year AHRC-funded programme investigating the interconnection between linguistic diversity and creativity. The programme is split into seven research strands, one of which is ‘Prismatic Translation’. In this post, Prof. Matthew Reynolds, Co-Investigator on the strand, explains how they have been looking at translations of Jane Eyre through a multilingual prism…
I spent March mainly in Pisa, working on fifteen Italian translations [of Jane Eyre] with a group of graduate students and early career researchers co-ordinated by our collaborator in the project there, Professor Alessandro Grilli.
It was an exhilarating experience, eight or ten of us grouped around a table in an airy room high up in an eighteenth-century palazzo overlooking the oldest botanical garden in Europe (even older than Oxford’s!) sharing our findings with the help of a projector pointed at the uneven wall.
Various discoveries emerged which will make their way into the webpages that are being created and book that is being written. The earliest Italian translation, done anonymously and published in Milan in 1904, mainly follows the 1854 French translation by Noémi Lesbazeilles (née Souvestre): for instance, Bertha Mason’s ‘red eyes’ become ‘yeux injectés’ and, in turn, ‘occhi iniettati’ (injected/blood-shot eyes’). Here we can see translation, not jumping from one language to another as though they were separate boxes, but moving through the continuum of language difference, following pathways in which Italian and French are joined.
Just occasionally, however, when the French was puzzling, the anonymous Italian translator turned to the English for help. When Jane hears Rochester’s voice telepathically calling across the moors, Charlotte Bronte wrote: ‘’O God! what is it?’ I gasped.’ Lesbazeilles-Souvestres takes this in a surprising direction: ‘J’aspirai l’air avec force’ (‘I breathed in forcefully / took a deep breath’). This must have struck the Italian translator as peculiar; the English must have been checked; and a simpler equivalent was found: ‘mormorai’ (‘I murmured’ – ‘gasped’, in its sense here, is a tricky word to match). Usually in translation – or at least in people’s ideas of translation – the translator works from the original and occasionally looks at other versions for help. But here we have the opposite: the French becomes the source text and the English serves as a guide to its interpretation.
One of the researchers, Caterina Cappelli, is someone I first met when she translated my novel The World Was All Before Them for her Masters thesis some years ago. Now, she has done an extraordinary piece of research, tracking the word ‘plain’ (also ‘plainly’ and ‘plainness’) through all its 49 appearances in the novel, in 13 different translations. That is, 637 occurrences of the word. As its frequency suggests, ‘plain’ is a crucial term for Brontë. Jane is plain (not beautiful), she speaks plainly (frankly), and she likes plain (simple) things; in the story, things are heard plainly (clearly) and become plain (are understood); and the novel itself is described as ‘a plain tale’ (a realist novel, that shows the world as it is).
One of Brontë’s ambitions in her writing was to re-assess this word, creating a woman character who can be admired for her mind and principles rather than her looks, and writing a story that can be valued for its truth-telling as much or more than for its excitements. For Brontë, ‘plain’ is what the literary critic William Empson called a ‘complex word’: a bundle of culturally-charged different meanings that need a whole play or novel to open up their synergies and contradictions.
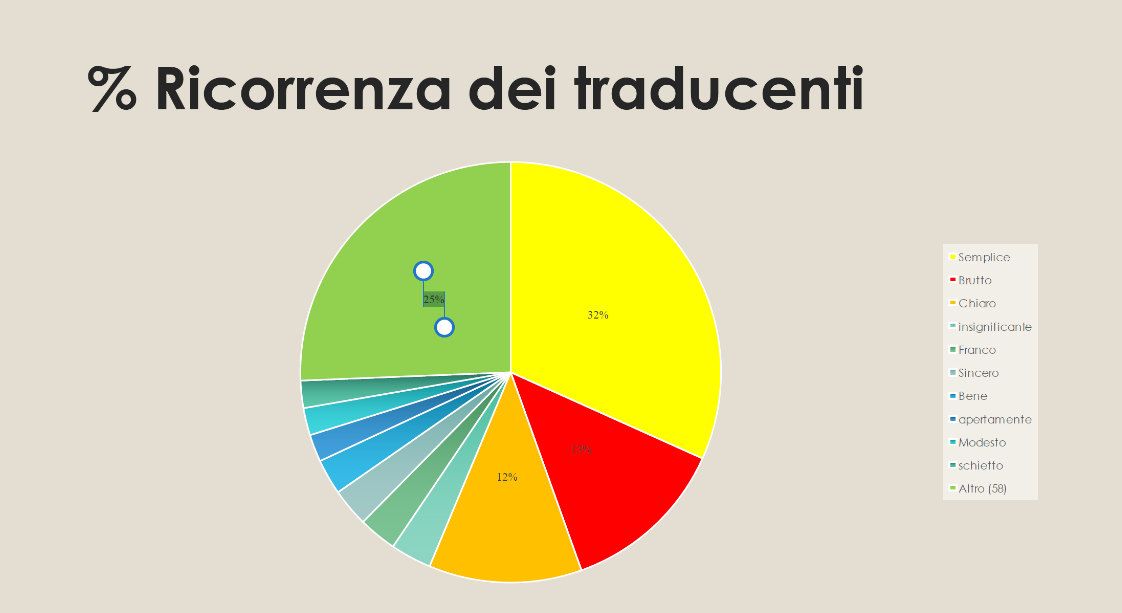
In the Italian translations, the explosion of meanings hidden in the word becomes, well, plain. This one English word is translated in – wait for it – sixty-eight quite different ways, in terms that correspond to: simple, ugly, clear, insignificant, sincere, well, open, modest, frank, easy, distinct, dull, common, smooth, white, and so on, and on. Here is a table constructed by Caterina:
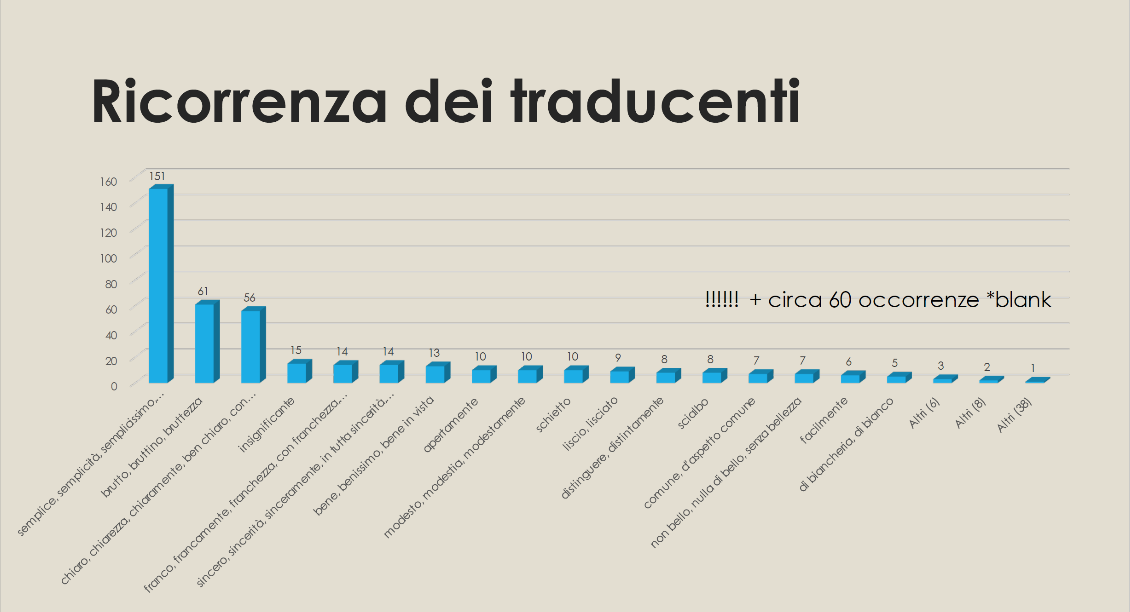
And here is a visualisation:
For more on Prismatic Translation, see their pages here.